Bertrand C. Carissimo, is a visiting research scientist from France (2000-2001). He has worked since 1988 in the research division of Electricite de France in applied meteorology and atmospheric dispersion. He received his Ph.D. in atmospheric and oceanic sciences and his M.A. in geophysical fluid dynamics from Princeton University.
His current research interests range from the evaluation and validation of models of atmospheric dispersion to the detailed numerical simulations of flow and dispersion in the canopy formed by large groups of buildings, as illustrated by the figure below, taken from preliminary simulations of the MUST experiment which were performed before the field campaign.
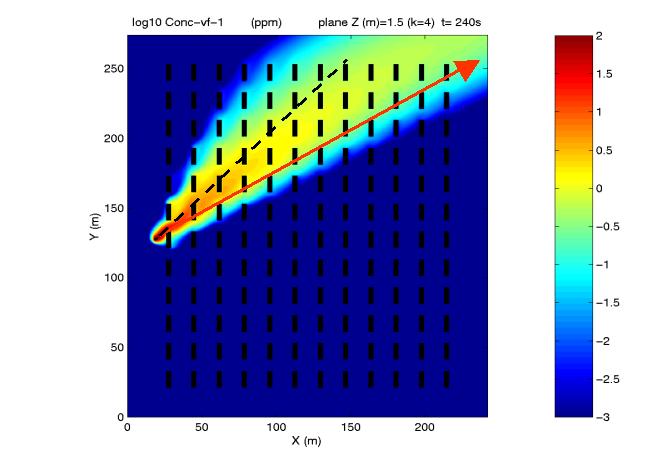
Figure 1 : Horizontal cross section of the simulated concentration field (ppm, log scale) from a release just upstream of a large obstacle array (in black on the picture) and for a wind speed of 3 m/s. The cross section is at a height of 1.5 m above the ground, which is the height of the release and half the total height of the obstacles. The simulations have been performed with a CFD model adapted to atmospheric conditions and with a k-epsilon turbulence closure. The horizontal resolution is 1m, requiring close to 2 million grid points for the calculation. The red arrow indicates the wind direction, at 30 deg. from the x direction and originates at the source; the black dashed line indicates the 45 deg. direction. Unlike the case of a free plume, which would be symmetrical relative to the wind axis, almost the entire plume, within the canopy formed by the array of obstacles, is located to the left of the red arrow.